Nakajima Homare
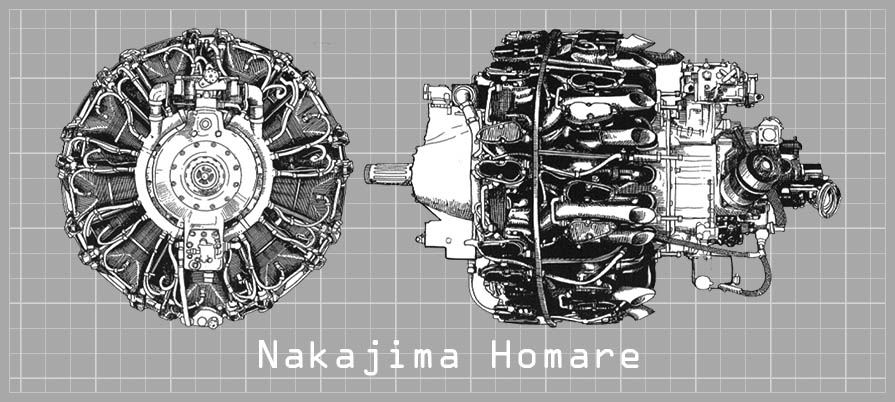
The Nakajima Homare (praise or honour) was an air-cooled twin-row 18 cylinder radial Japanese aircraft engine manufactured by the Nakajima Aircraft Company. Producing almost 2,000 horsepower, it was used widely by both the Imperial Japanese Army and the Imperial Japanese Navy. Given the Navy service designation NK9, the "Homare" was also given the company designation NBA, Army experimental designation Ha-45 or, Army long designation Nakajima Army Type 4 1,900 hp Air-Cooled Radial and, (coincidentally), unified designation code of Ha-45.
Mitsubishi Homare
Design and development
Development of the Homare started in 1940, and certification was completed in 1941. It succeeded Nakajima's previous 14 cylinder Sakae (Ha-25) engine, which had its own forward seven cylinders staggered from the rear seven for efficient cooling. The design was exceptionally compact, with an external diameter of 118 cm, a mere 3 cm larger than the Sakae. With a bore and stroke of 130 mm x 150 mm, it was classified as a short-stroke engine. It was designed to output around 1800 hp (1340 kW), or 100 hp (75 kW) per cylinder. However, the tight design of the engine made it difficult to maintain quality in manufacturing, and unreliability in the field was a significant problem; actual output of early models at altitude was in the range of 1300 hp (970 kW), far below the designed capability. Later models had improved performance, and it became one of the predominant powerplants of Japanese military aircraft in the latter part of the war. A total of 9089 were produced. Variants
General characteristics
- Type: 18-cylinder air-cooled twin-row radial engine
- Bore: 130 mm (5.12 in)
- Stroke: 150 mm (5.91 in)
- Displacement: 35.8 L (2187 in³)
- Length: 1,778 mm (70 in)
- Diameter: 1,180 mm (46.5 in)
- Dry weight: 810 kg (1,785 lb)

Mitsubishi Homare
Development of the Homare started in 1940, and certification was completed in 1941. It succeeded Nakajima's previous 14 cylinder Sakae (Ha-25) engine, which had its own forward seven cylinders staggered from the rear seven for efficient cooling. The design was exceptionally compact, with an external diameter of 118 cm, a mere 3 cm larger than the Sakae. With a bore and stroke of 130 mm x 150 mm, it was classified as a short-stroke engine. It was designed to output around 1800 hp (1340 kW), or 100 hp (75 kW) per cylinder. However, the tight design of the engine made it difficult to maintain quality in manufacturing, and unreliability in the field was a significant problem; actual output of early models at altitude was in the range of 1300 hp (970 kW), far below the designed capability. Later models had improved performance, and it became one of the predominant powerplants of Japanese military aircraft in the latter part of the war. A total of 9089 were produced. Variants
- Homare 11 - 1,650 hp (1,230 kW), 1,820 hp (1,357 kW), 1,900 hp (1,417 kW)
- Homare 12 - 1,825 hp (1,361 kW)
- Homare 21 - 2,000 hp (1,491 kW)
- Homare 23 - 2,000 hp (1,491 kW)
General characteristics
- Type: 18-cylinder air-cooled twin-row radial engine
- Bore: 130 mm (5.12 in)
- Stroke: 150 mm (5.91 in)
- Displacement: 35.8 L (2187 in³)
- Length: 1,778 mm (70 in)
- Diameter: 1,180 mm (46.5 in)
- Dry weight: 810 kg (1,785 lb)
Components
- Valvetrain: push rod operated overhead-valve system with 2 valves per cylinder
- Supercharger: Two-speed single stage centrifugal
- Fuel system: 2 BBL. D.D. Float Carb.
- Fuel type: 92 Octane + ADI
- Cooling system: Air-cooled
Performance
- Power output: 1,485 kW (1,990 hp) at altitude
- Specific power: 38,57 kW/L (0.91 hp/in³)
- Compression ratio: 8.0
- Power-to-weight ratio: 1.83 kW/kg (1,11 hp/lb)
|
|
Source(s):
Wikipedia
Gunston, Bill (2006). World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines: From the Pioneers to the Present Day (5th ed.). Stroud, UK: Sutton. ISBN 0-7509-4479-X.
Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II. London. Studio Editions Ltd, 1989. ISBN 0-517-67964-7
Francillon, Ph.D., René J. Japanese Aircraft of the Pacific War. London: Putnam & Company Ltd., 2nd edition 1979. ISBN 0-370-30251-6.
Wikipedia
Gunston, Bill (2006). World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines: From the Pioneers to the Present Day (5th ed.). Stroud, UK: Sutton. ISBN 0-7509-4479-X.
Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II. London. Studio Editions Ltd, 1989. ISBN 0-517-67964-7
Francillon, Ph.D., René J. Japanese Aircraft of the Pacific War. London: Putnam & Company Ltd., 2nd edition 1979. ISBN 0-370-30251-6.






