POWERPLANTS RESOURCE CENTER > GERMANY > PREVIOUS PAGE
Development of the Junkers diesel engines started in the 1920s with the Junkers Fo3 and Junkers Fo4/Junkers SL1. The Fo4 was re-designated Junkers 4, which in turn was re-designated Junkers Jumo 204 by the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM), where the first number indicates the manufacturer; 2 – Junkers Motoren.
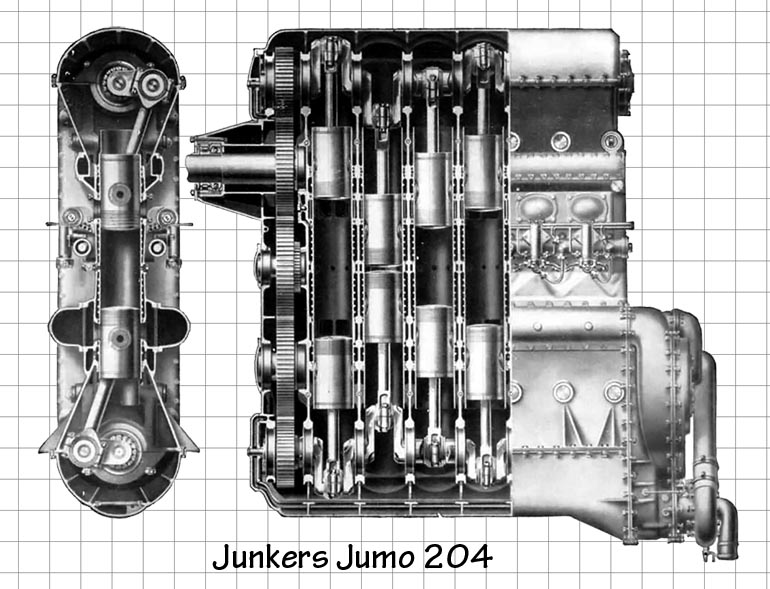
These engines all used a two-stroke cycle with six cylinders and twelve pistons, in an opposed piston configuration with two crankshafts, one at the bottom of the cylinder block and the other at the top, geared together. The pistons moved towards each other during the operating cycle. Intake and exhaust ports were duplicated at both ends of the block. There were two cam-operated injection pumps per cylinder, each feeding two nozzles, totaling four nozzles per cylinder.
[Source: Unknown]
The Jumo 204 solved this problem to a very large degree through a better arrangement of the ports. The intake port was located under the "lower" piston, while the exhaust port was under the "upper". The lower crankshaft ran eleven degrees behind the upper, meaning that the exhaust ports opened first, allowing proper scavenging. This system made the two-stroke Jumos run as cleanly as four-stroke engines using valves, but with considerably less complexity.
The Jumo 204 (originally designated Jumo 4) was test flown in early 1929 installed in a Junkers G 24.
The Jumo Fo3 and 204 were licensed to Napier & Son, who built a small number as the Napier Culverin just prior to the war. Late in the war, they mounted three Culverins in a triangle layout to produce the Napier Deltic, which was for some time one of the most powerful and compact diesel engines in the world.
Specifications:
Type: Six-cylinder 12-piston liquid-cooled opposed piston inline
two-stroke diesel engine
Bore: 120 mm (4.72 in)
Stroke: 210 mm (8.27 in)
Displacement: 28.5 l (1,739 in³)
Length: 1,260 mm (49.61 in)
Width: 510 mm (20.08 in)
Height: 1,510 mm (59.45 in)
Dry weight: 750 kg (1,653 lb)
Performance
Power output: 552 kW (740 hp) at 1,800 rpm
Specific power: 19.3 kW/l (0.42 hp/in³)
Compression ratio: 17:1
Specific fuel consumption: 212 g/(kW•h) (0.35 lb/(hp•h))
Power-to-weight ratio: 0.74 kW/kg (0.45 hp/lb)
Applications:
• Blohm & Voss BV 138
• Junkers Ju 52/1mdo testbed
• Junkers Ju 86
• Mitsubishi Ki-20
Sources:
Wikipedia
POWERPLANTS RESOURCE CENTER > GERMANY > PREVIOUS PAGE
